Exploring Blockchain Technology
2025-11-09
Blockchain technology is transforming myriad sectors, but none more so than finance. With its potential to create a more transparent, efficient, and secure financial environment, blockchain is reshaping how money is processed, stored, and transferred globally. This article explores how blockchain technology is driving change in the financial sector, its implications for the future, and answers several pertinent questions regarding its integration into financial services.
At its core, blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across many computers in such a way that the registered transactions cannot be altered retroactively. This technology is based on a consensus mechanism involving nodes (participants) that validate and confirm transactions. The immutability and transparency of blockchain render it an appealing solution for the financial sector, which traditionally relies on centralized authorities.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are perhaps the most recognizable applications of blockchain. However, its utility extends far beyond digital currencies. Blockchain's distributed ledger technology (DLT) allows for the creation of smart contracts, improves data security, and facilitates real-time clearing and settlement, making it a revolutionary force in finance.
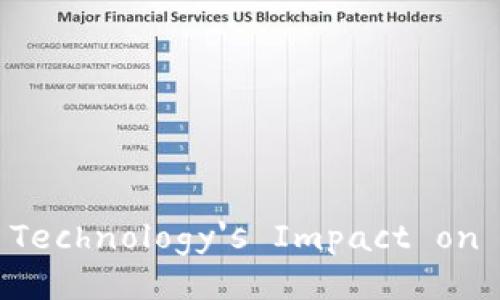
In recent years, there has been a surge in the adoption of blockchain technology across financial institutions. Major banks and fintech companies are exploring blockchain for diverse applications including cross-border payments, trade finance, and identity verification. Initiatives such as the Bank of England’s use of blockchain for payment systems, and Ripple’s network for cross-border transactions, exemplify the growing acceptance of this technology.
Additionally, global regulatory bodies are beginning to formulate frameworks for integrating blockchain solutions into existing financial systems. While there are hurdles, including regulatory concerns and technology integration, the momentum is palpable, suggesting that blockchain is poised to play a central role in the future of finance.
Why is blockchain technology garnering the attention of the financial sector? Here are four benefits that highlight its value:
Blockchain offers enhanced security features that traditional systems lack. Each transaction on a blockchain is encrypted and linked to the previous transaction, thus creating a chain of data that is extremely difficult for malicious actors to alter. This reduces risk and fosters trust. Financial institutions can leverage these features to protect sensitive data and prevent fraud.
The transparency of blockchain is another crucial benefit. All transactions are recorded on a public ledger that stakeholders can access in real time. This level of transparency can increase accountability, reduce reconciliation errors, and improve trust between financial institutions and their customers.
Blockchain technology can reduce operating costs associated with transaction processing and record-keeping. By eliminating intermediaries and streamlining processes, financial institutions can drastically lower overhead costs. Moreover, smart contracts automate and expedite contract performance, reducing delays and further enhancing efficiency.
Blockchain enables real-time transaction processing and settling, revolutionizing how cross-border payments are executed. Traditional methods can take days for funds to clear, while blockchain can achieve near-instantaneous transfers, providing significant benefits for businesses and individuals alike, especially in time-sensitive transactions.

As the adoption of blockchain technology becomes more pervasive in the financial sector, there is a growing need for industry professionals to be well-versed in its applications and implications. Education and training programs focused on blockchain are starting to emerge, equipping finance professionals with essential knowledge to successfully navigate this evolving landscape.
Courses on blockchain cover various aspects, including the underlying technology, use cases in finance, compliance and regulatory issues, and potential challenges. Familiarity with coding languages commonly used in blockchain development, such as Solidity (for Ethereum), is also becoming advantageous for finance professionals. Training in this domain not only enhances career prospects but also empowers individuals and organizations to innovate and harness the full potential of blockchain technology.
Despite its impressive potential and benefits, blockchain technology also faces several challenges that can hinder its widespread integration in the financial sector:
The regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain and cryptocurrencies remains unclear in many regions. Financial institutions must navigate a patchwork of laws and regulations that differ considerably from one jurisdiction to another, complicating compliance efforts.
Many financial institutions operate on legacy systems that may not easily integrate with blockchain technology. The expense and resources required for a complete overhaul can be substantial, and there can be considerable resistance to change from stakeholders within the organization.
Some blockchain platforms face limitations regarding transaction throughput, which can become problematic as usage scales. Solutions like second-layer networks are being developed to address this issue, but they are still in development and require full validation.
While blockchain itself offers enhanced security, the broader cybersecurity landscape presents risks. New attack vectors emerge as blockchain systems are integrated into existing infrastructures. Ensuring that the entire ecosystem remains secure is a considerable concern for IT professionals.
Looking forward, the integration of blockchain technologies in finance is expected to deepen, driven by ongoing innovations, regulatory developments, and growing institutional support. The future may see the emergence of more decentralized financial services (DeFi), where traditional services like lending, trading, and insurance can be performed without intermediaries.
Furthermore, central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) are gaining traction worldwide. Many central banks are exploring harnessing blockchain for issuing digital currency, which could revolutionize how governments conduct monetary policy and manage economic stability.
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, it has the potential to redefine the financial landscape, leading to increased efficiency, security, and accessibility. Financial institutions must remain adaptive, innovative, and proactive, ensuring that they are positioned to leverage these changes to their advantage.
Blockchain enhances security by decentralizing the storage of transaction records, meaning that no single entity has control over the data. Each transaction is encrypted and time-stamped, and once confirmed, it becomes part of the immutable ledger. This structure makes it extremely difficult for hackers to alter transaction data. Additionally, the consensus mechanism requires multiple nodes to validate transactions before they are added to the chain, further safeguarding the integrity of the data.
Common use cases for blockchain technology in finance include cross-border payments, where blockchain's speed and low fees are advantageous; trade finance, which benefits from enhanced transparency and reduced fraud; and identity verification processes that can streamline KYC (Know Your Customer) compliance. Furthermore, institutional investment in cryptocurrencies and tokenization of assets represent growing areas where blockchain is impactful.
Financial institutions face several challenges when adopting blockchain, including regulatory hurdles associated with the broader cryptocurrency landscape, integration issues stemming from reliance on legacy infrastructure, and security concerns related to the deployment of new technology. Additionally, the volatile nature of cryptocurrencies can deter banks from fully embracing the technology, despite its potential for innovation.
While blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize many aspects of finance, a complete replacement of traditional banking systems is unlikely in the near term. Instead, we can expect a hybrid model where traditional banks and blockchain-based financial systems coexist, leveraging each other’s strengths. The future of finance may involve enhanced collaboration between fintech innovations and traditional banking practices.
In conclusion, blockchain technology is undeniably reshaping the financial services ecosystem. Its benefits, while substantial, are accompanied by challenges that require careful consideration and tactical responses from industry leaders. As the landscape evolves, remaining agile and informed will be paramount for financial professionals navigating this disruption.